Transportation STEAMventures
- Grades: TK-K
- Number of Students: Up to 30
- Number of Lessons: 12
- Hours of Content: 12+
- Additional Resources: Curriculum Sample
Highlights:
STEAMventures: Fueling Curiosity, Igniting Innovation
All aboard for a STEAM-powered transportation adventure designed specifically for transitional and kindergarten students. Young minds engineer and design boats and trains in this immersive and interactive enrichment program. Through dynamic scientific exploration, artistic expression and problem-solving challenges, the step-by-step lessons foster foundational math and English Language Arts skills.
This fun, engaging experience embraces play, movement and creativity, equipping young learners with the skills needed for elementary school. Set sail for an interactive and collaborative journey where the fusion of exploration and hands-on activities propels students into the captivating worlds of locomotion.
Recommended Setting:
- Summer Camps
- Classrooms
- Out-of-School Time Programs
Curriculum or Lesson Topics:
Subject Targets:
- Physical Science
- Technology
- Engineering Design
- Art/STEAM
- Math
- English Language Arts
Curriculum Topics:
- Brick Sorting
- Alphabet Adventures
- Parts of Trains and Boats
- Brick Builds
- Using our Senses
- Engineering Exploration
- Transcontinental Railroad
- Artistic Creations
- Mathematician's Challenge
- Career Exploration
- Let’s Go on an Outing!
- Transportation Celebrations
Standard Alignments:
Habits of Mind:
16 thinking habits developed by Art Costa and Bena Kallick to empower students to succeed in a 21st-century learning environment.
- Managing Impulsivity
- Thinking Interdependently
- Striving for Accuracy
- Applying Past Knowledge to New Situations
- Gathering Data through All Senses
- Creating, Imagining, Innovating
- Taking Responsible Risks
- Finding Humor
- Listening with Understanding and Empathy
- Thinking and Communicating with Clarity and Precision
- Responding with Wonderment and Awe
- Persisting
- Thinking about Your Thinking (Metacognition)
- Remaining Open to Continuous Learning
- Questioning and Posing Problems
- Thinking Flexibly
21st Century Skills:
A set of widely-applicable abilities essential for success in the information age.
- Communication and Collaboration
- Critical Thinking and Problem Solving
- Information, Media, and Technology Literacy
- Initiative and Self-Direction
- Creativity and Innovation
- Social and Cross-Cultural Skills
- Leadership and Responsibility
- Flexibility and Adaptability
- Productivity and Accountability
© 2019 Battelle for Kids. battelleforkids.org. All Rights Reserved. Battelle for Kids was not involved in the production of this product and does not endorse it.
Next Generation Science Standards:*
- NGSS Core Idea ETS1.A: Defining Engineering Problems
- NGSS K-2-ETS1-1: Engineering Design
- NGSS K-2-ETS1-3: Engineering Design
- NGSS K-PS2-2: Forces and Motion
* Next Generation Science Standards and NGSS is a registered trademark of WestEd. Neither WestEd nor the lead states and partners that developed the Next Generation Science Standards were involved in the production of this product, and do not endorse it.
Common Core State Standards for Mathematics:
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.K.CC.A.1: Count to 100 by ones and by tens.
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.K.CC.A.2: Count forward beginning from a given number within the known sequence (instead of having to begin at 1).
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.K.CC.B.4.B: Understand that the last number name said tells the number of objects counted. The number of objects is the same regardless of their arrangement or the order in which they were counted.
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.K.CC.B.4: Understand the relationship between numbers and quantities; connect counting to cardinality.
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.K.CC.B.5: Count to answer "how many?" questions about as many as 20 things arranged in a line, a rectangular array, or a circle, or as many as 10 things in a scattered configuration; given a number from 1-20, count out that many objects.
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.K.CC.C.6: Identify whether the number of objects in one group is greater than, less than, or equal to the number of objects in another group, e.g., by using matching and counting strategies.
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.K.G.A.1: Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes, and describe the relative positions of these objects using terms such as above, below, beside, in front of, behind, and next to.
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.K.G.A.2: Correctly name shapes regardless of their orientations or overall size.
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.K.G.B.4: Analyze and compare two- and three-dimensional shapes, in different sizes and orientations, using informal language to describe their similarities, differences, parts (e.g., number of sides and vertices/"corners") and other attributes (e.g., having sides of equal length).
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.K.G.B.5: Model shapes in the world by building shapes from components (e.g., sticks and clay balls) and drawing shapes.
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.K.G.B.6: Compose simple shapes to form larger shapes. For example, "Can you join these two triangles with full sides touching to make a rectangle?"
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.K.MD.A.1: Describe measurable attributes of objects, such as length or weight. Describe several measurable attributes of a single object.
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.K.MD.A.2: Directly compare two objects with a measurable attribute in common, to see which object has "more of"/"less of" the attribute, and describe the difference. For example, directly compare the heights of two children and describe one child as taller/shorter.
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.K.MD.B.3: Classify objects into given categories; count the numbers of objects in each category and sort the categories by count.
© Copyright 2010. National Governors Association Center for Best Practices and Council of Chief State School Officers. All rights reserved.
Common Core State Standards for English Language Arts:
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.L.K.1.A: Print many upper- and lowercase letters.
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.L.K.4.A: Identify new meanings for familiar words and apply them accurately (e.g., knowing duck is a bird and learning the verb to duck).
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.L.K.5.A: Sort common objects into categories (e.g., shapes, foods) to gain a sense of the concepts the categories represent.
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.L.K.5.C: Identify real-life connections between words and their use (e.g., note places at school that are colorful).
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.L.K.6: Use words and phrases acquired through conversations, reading and being read to, and responding to texts.
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.K.1.A: Follow words from left to right, top to bottom, and page by page.
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.K.1.B: Recognize that spoken words are represented in written language by specific sequences of letters.
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.K.2.B: Count, pronounce, blend, and segment syllables in spoken words.
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.K.2.D: Isolate and pronounce the initial, medial vowel, and final sounds (phonemes) in three-phoneme (consonant-vowel-consonant, or CVC) words. (This does not include CVCs ending with /l/, /r/, or /x/.)
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.K.3.A: Demonstrate basic knowledge of one-to-one letter-sound correspondences by producing the primary sound or many of the most frequent sounds for each consonant.
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.K.4: Read emergent-reader texts with purpose and understanding.
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.SL.K.1.A: Follow agreed-upon rules for discussions (e.g., listening to others and taking turns speaking about the topics and texts under discussion).
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.SL.K.1.B: Continue a conversation through multiple exchanges.
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.SL.K.2: Confirm understanding of a text read aloud or information presented orally or through other media by asking and answering questions about key details and requesting clarification if something is not understood.
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.SL.K.4: Describe familiar people, places, things, and events and, with prompting and support, provide additional detail.
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.SL.K.5: Add drawings or other visual displays to descriptions as desired to provide additional detail.
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.SL.K.6: Speak audibly and express thoughts, feelings, and ideas clearly.
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.K.3: Use a combination of drawing, dictating, and writing to narrate a single event or several loosely linked events, tell about the events in the order in which they occurred, and provide a reaction to what happened.
© Copyright 2010. National Governors Association Center for Best Practices and Council of Chief State School Officers. All rights reserved.
International Society for Technology in Education:
- 1.3.c Curate Information: Students curate information from digital resources using a variety of tools and methods to create collections of artifacts that demonstrate meaningful connections or conclusions.
- 1.3.d Explore Real-World Issues: Students build knowledge by actively exploring real-world issues and problems, developing ideas and theories, and pursuing answers and solutions.
- 1.4.a Design Process: Students know and use a deliberate design process for generating ideas, testing theories, creating innovative artifacts or solving authentic problems.
- 1.4.b Design Constraints: Students select and use digital tools to plan and manage a design process that considers design constraints and calculated risks.
- 1.4.c Prototypes: Students develop, test and refine prototypes as part of a cyclical design process.
- 1.6.a Choose Platforms or Tools: Students choose the appropriate platforms and tools for meeting the desired objectives of their creation or communication.
- 1.6.c Models and Visualizations: Students communicate complex ideas clearly and effectively by creating or using a variety of digital objects such as visualizations, models or simulations.
- 1.7.c Project Teams: Students contribute constructively to project teams, assuming various roles and responsibilities to work effectively toward a common goal.
- 1.7.d Local and Global Issues: Students explore local and global issues, and use collaborative technologies to work with others to investigate solutions.
ISTE Standards for Students, ©2016, ISTE® (International Society for Technology in Education), iste.org. All rights reserved. ISTE was not involved in the production of this product and does not endorse it.
National Core Arts Standards:
- VA:Cn10.1.Ka: Create art that tells a story about a life experience.
- VA:Cn10.1.Pka: Explore the world using descriptive and expressive words and art-making.
- VA:Cn11.1.Ka Identify a purpose of an artwork.
- VA:Cn11.1.Pka: Recognize that people make art.
- VA:Cr1.1.Ka Engage in exploration and imaginative play with materials.
- VA:Cr1.1.Ka: Use various materials and tools to create artworks.
- VA:Cr1.2.Ka Engage collaboratively in creative art-making in response to an artistic problem.
- VA:Cr1.2.PKa Engage in self directed, creative making.
- VA:Cr1.K: Generate and conceptualize artistic ideas and work.
- VA:Cr2.1.Ka: Through experimentation, build skills in various media and approaches to artmaking.
- VA:Cr2.1.PKa Use a variety of artmaking tools
- VA:Cr2.2.Ka: Identify safe and non-toxic art materials, tools, and equipment.
- VA:Cr2.2.PKa: Share materials with others.
- VA:Cr2.3.Ka: Create art that represents natural and constructed environments.
- VA:Cr2.3.PKa: Create and tell about art that communicates a story about a familiar place or object.
- VA:Cr3.1.PKa: Share and talk about personal artwork.
- VA:Re.7.2.Ka: Describe what an image represents.
National Core Arts Standards © 2015 National Coalition for Core Arts Standards. Rights administered by Young Audiences, Inc. New York, NY. https://www.nationalartsstandards.org
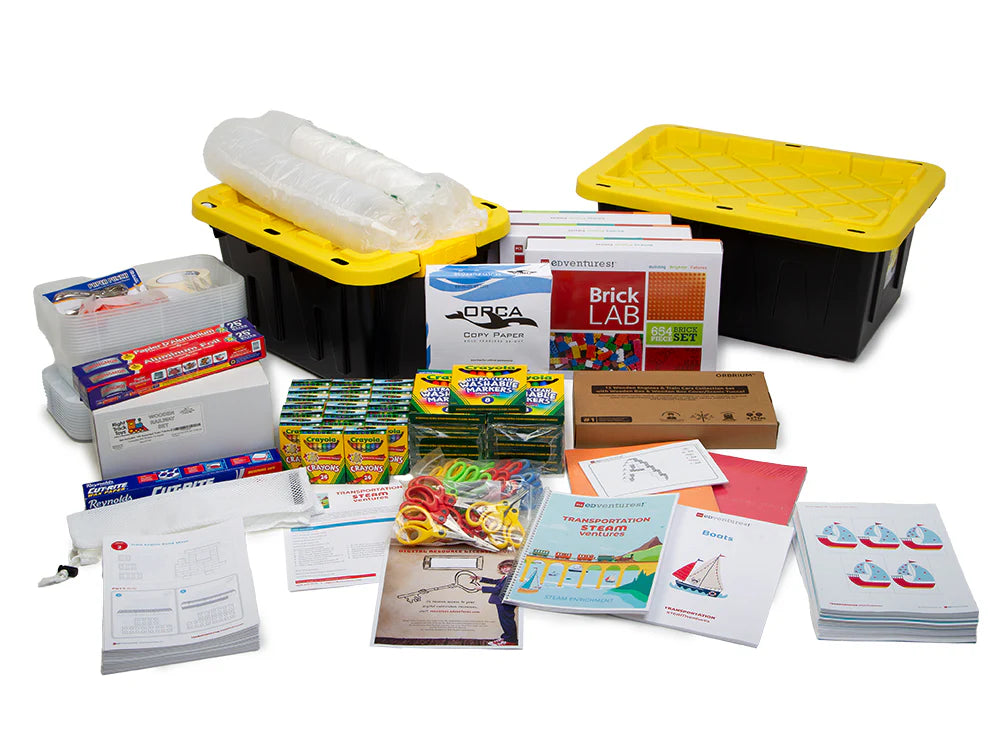
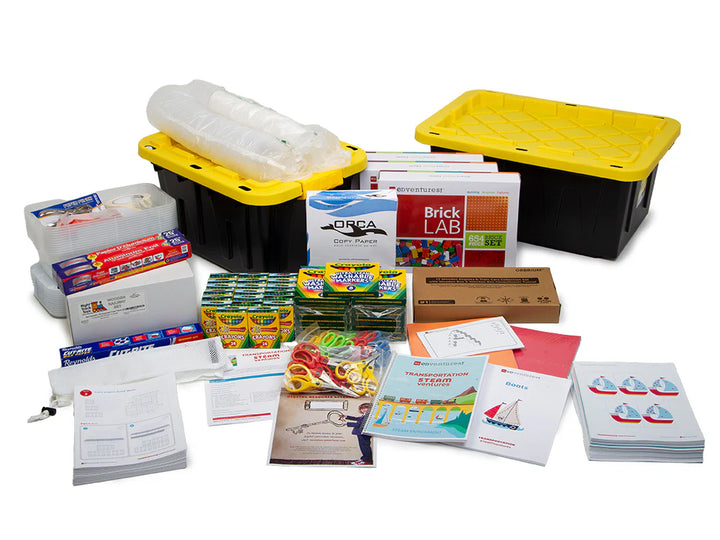
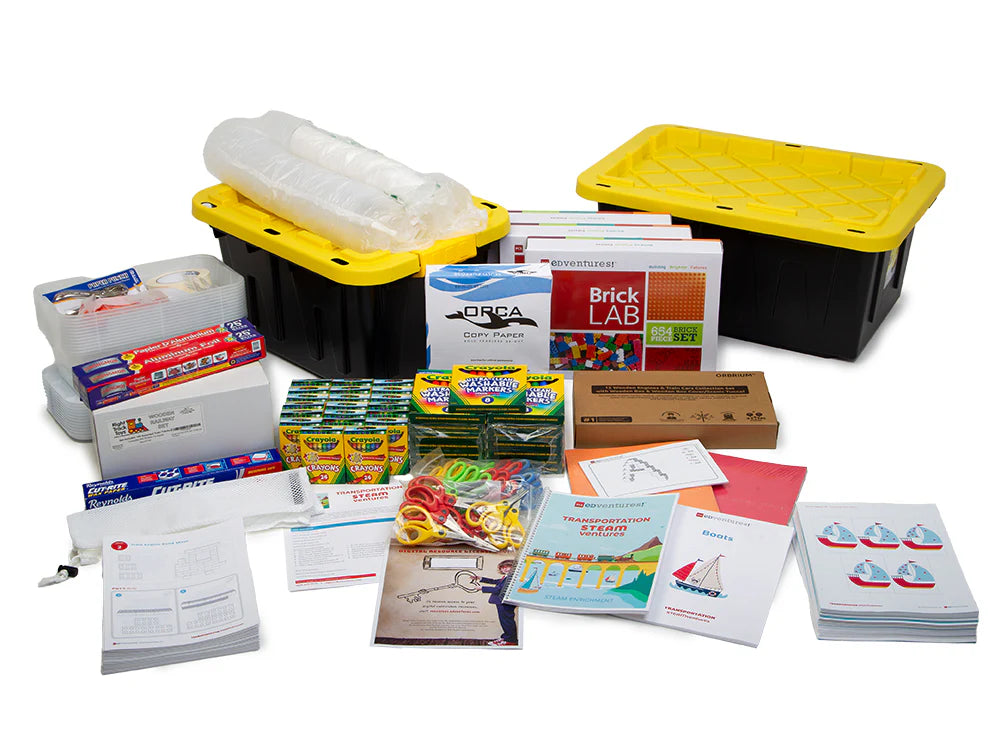
What's Included:
Each Lesson Includes:
- Schedule
- Opening & Closing Discussion
- Step-By-Step Activity Instructions
- Topic Background Information & Vocabulary
- Materials List
Complete Program Includes:
- Instructor Guide: 1
- BrickLAB Charade Card Set: 1
- Sets of Builds: 15
- Sets of Consumable Student Pages: 30
- Sets of Reusable Student Pages: 4
- Storage Bins with Lids: 2
- Aluminum Foil - Roll (50 ft): 1
- Mesh Bag (for cleaning bricks):1
- Sets of BrickLAB Bricks: 3
- Brick Separator (for deconstructing builds):1
- Clear, Round Containers (50 pack): 2
- Small Storage Containers with Lids: 12
- Crayons (24 pack): 20
- Paper Cups (4 oz): 50
- Geometric Die Cut Shapes (25+ pack) :1
- Glue Sticks: 30
- Hole Punch:1
- Marbles (20 ct): 2
- Washable Markers, Broad Line (8 pack): 15
- White Copy Paper (500 pack): 1
- Construction Paper (assorted colors, 50 sheets): 2
- Roll of Wax Paper: 1
- Golf Pencils (50+ pack): 1
- Rubberbands (250 pk): 1
- Scissors - Adult: 1
- Scissors - Children: 30
- Roll of Masking Tape: 1
- Metal Washers: 80
- Wooden Train Tracks (55 pcs): 2
- Wooden Toy Trains (12 pcs): 1
- Access to Digital Resource Portal